Business
Solution For the Earth DYC
Solution For the Earth DYC
| Enhancement of air pollutant regulations |
Enhancement of emissio standards |
Increased nitrogen and sulfur oxides (NOx, SOx) emissions |
Increasing need for pollutant treatment technology development |
|---|---|---|---|
| With increasing interest in environmental issues, regulations on air pollutants are being strengthened at the country and abroad |
The Ministry of Environment reinforced air emission standards for major air pollutants such as nitrogen and sulfur oxides, dust in 2010 |
85% of the energy used on the planet are fossil fuels that emit nitrogen and yellow dust, and are mainly used in thermal power plants, steel plants and incinerators. It is responsible for respiratory diseases, photochemical smog, and acid rain. |
simultaneous removal technology for nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides with different characteristics.
☞ It is judged that the development of efficient low-cost and eco-friendly treatment technology for exhaust gas is a national urgent task. |
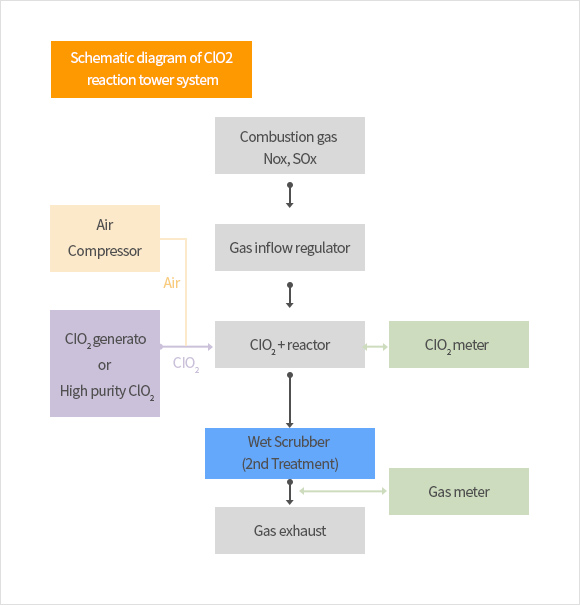
| Existing treatment technology | Mechanism to reduce fine dust using chlorine dioxide Mechanism |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Selective catalytic reduction method | Wet scrubbing method | Activated carbon adsorption method | |
| Operation cost is low, but equipment cost is excessive. In addition, there is a disadvantage of generating particulate matter and high temperature (300~400℃) treatment. |
Various applications are advantageous, but multi-step treatment and generated large amounts of liquid waste are disadvantages | Facility cost is low, but treatment efficiency is low (60 ~ 70%). In addition, only a small amount of combustion gas can be treated, and large-capacity waste combustion gas cannot be treated. | Equipment cost is very low due to rapid oxidation reaction, and its treatment efficiency is higher than that of the existing method. So it can be applied in a variety of ways. No by-products such as metal or gas are generated, and wastewater is reduce |
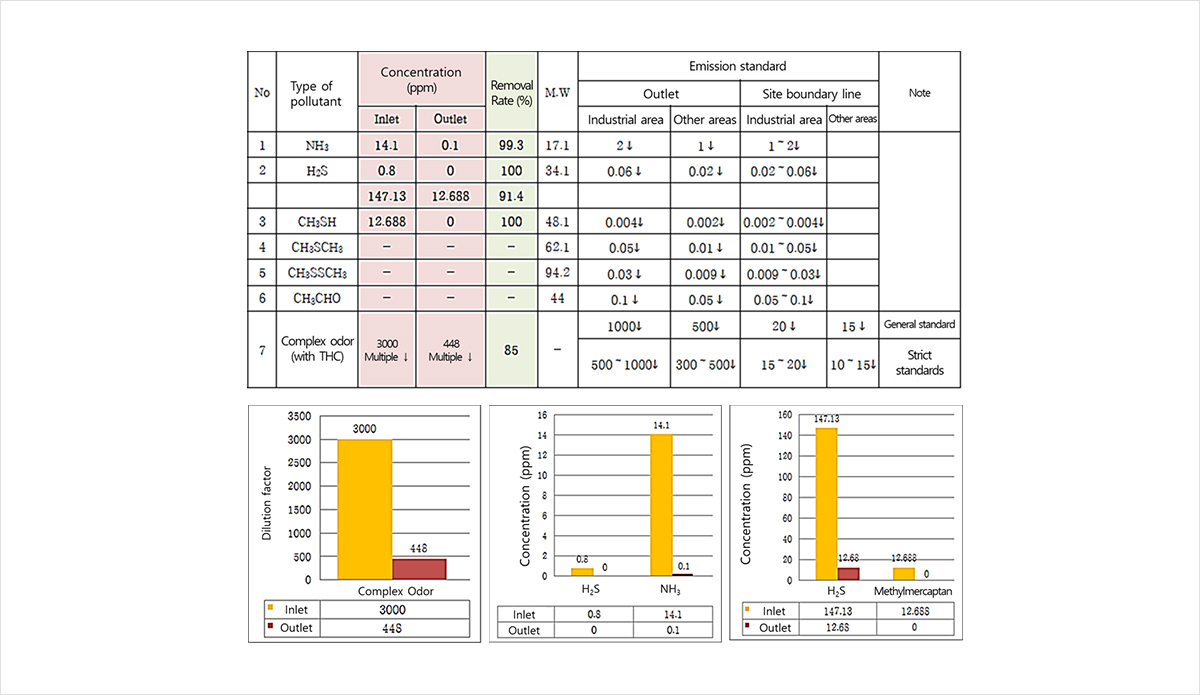
| Div. | NO | SO2 |
|---|---|---|
| Incoming concentration (ppm) | 400 | 200 |
| After the first dry treatment (ppm) |
80 | 40 |
| Removal rate (%) | 80% | 80% |
| After the 2nd wet treatment (ppm) |
40 | 20 |
| Removal rate (%) | 90% | 90% |
| Total removal rate (%) | 90% | 90% |